Methods
To understand how the brain supports perception and cognition, we need to build computational models of brain information processing and test these models against brain and behavioural data.
Work in the lab focuses on systems-level models that can learn to perform real-life tasks, such as object recognition and decision making.
We use psychophysics and functional magnetic resonance imaging to measure human brain activity and behaviour on real-life tasks. We use artificial neural networks as computational models, and develop analysis methods for testing how well different models predict the measured brain activity and behaviour.
Vision
How does the brain make sense of the outside visual world? Our work suggests that deep convolutional neural networks may provide a computationally explicit model of how the visual system transforms incoming visual signals into a meaningful representation of the outside world. The figure below summarizes our findings, which show that visual objects are represented similarly in a deep neural network, in human visual cortex, and in perception. In all three, objects cluster according to natural categories, such as faces and bodies.
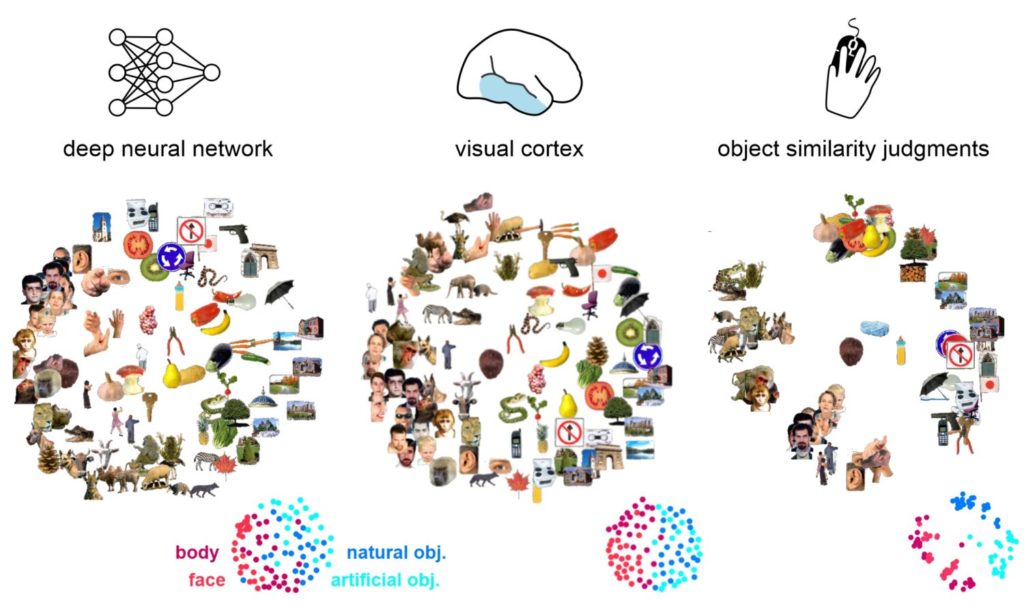
These findings are exciting because they suggest that an artificial neural network built to loosely match the architecture of the visual system, and trained to categorize objects, develops human-like object representations. However, deep neural networks are still far from being human. Current work in the lab focuses on improving artificial neural networks as models of the brain by more closely simulating real-life visual experience and learning goals during training.
Cognition
How do we remember the recent past, make decisions, and execute plans? Our cognitive abilities rely heavily on a network of frontal and parietal brain regions. However, the internal workings of this network are not well understood. Current work in the lab focuses on extending our approach beyond vision to understand how frontoparietal cortex supports a range of high-level cognitive functions.
